Homologa compiles data from different sources from over 120 countries. Each data source has its own structure and unfortunately data quality is not homogeneous throughout the different sources due to different languages, structure, units, and even cultural differences.
The Homologa team thoroughly analyses each one of the sources and defines a process to transform the data obtained into a fully developed and 100% compatible dataset ready to be loaded into the Homologa database. This process will transform an initially incoherent and not comparable data file into a fully harmonized, up-to-date and globally comparable dataset. This process defines the Homologa Data Lifecycle.
The Homologa Data Lifecycle is data process consisting of four separate phases. Lifecycle refers to the progression of data from its inception to its final use. The four different phases are as follows:
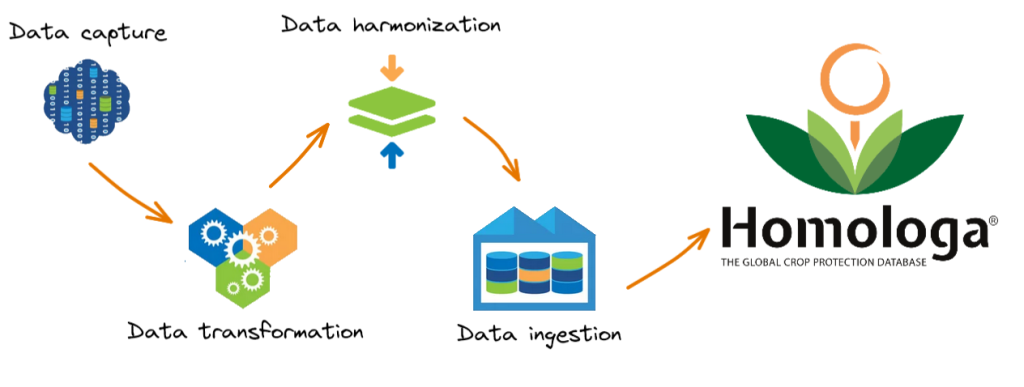
1.- Data capture: Data capture is a process in which data is extracted from each of the original data sources. Our team implements tailored solutions by using the most appropriate technology depending on the data source design.
There are three main data capture methods:
- Manual: this is the most tedious and time-consuming method, and therefore the most expensive due to the need of investing in data entry specialist time.
- Combined: In some cases, the source of the data (batch files) is provided by an official (and even validated) source which provides a solid start. However, this data normally has to go through different manipulation stages before it can be implemented into Homologa’s structure.
- Automated: this method uses scraping and parsing tools providing an affordable and scalable solution with high quality output. In addition, these tools generate files with the proper structure needed for a direct implementation into Homologa.
2.- Data transformation: during this process (aka, Transform and Load (ETL)), data undergoes a full transformation which will implement the most adequate format, structure or values required during the following stages. Different tools are used during this process such Talend Studio, SQL, Python, etc. and they are mainly focused on reducing data redundancy and improving the overall data quality.
3.- Data harmonization: data harmonization is a process which entails the unification of data fields, formats, dimensions, and columns into a composite dataset. You can find more information about this particular process in our blog post “Harmonization process in Homologa”.
4.- Data ingestion: during this last stage, the final files are compiled and they include all the required structure and ontologies needed for 100% integration and storage in Homologa.
All in all, these four phases allow Homologa to offer the upmost quality for global, up-to-date and harmonized regulatory information in the market. Contact us or visit Homologa® for further details about our Homologa Data Lifecycle process or about any of our services or datasets.
Source: Adobe stock

